Operating Cost
By CHRIS B MURPHY
Reviewed By AMY DRURY
Updated Jul 27, 2020
营业成本
作者:Chris B Murphy
审核人:Amy Drury
更新时间:2020年7月27日
What Are Operating Costs?
什么是营业成本?
Operating costs are associated with the maintenance and administration of a business on a day-to-day basis. Operating cost is a total figure that include direct costs of goods sold (COGS) from operating expenses (which exclude direct production costs), and so includes everything from rent, payroll, and other overhead costs to raw materials and maintenance expenses. Operating costs exclude non-operating expenses related to financing such as interest, investments, or foreign currency translation.
营业成本与企业日常业务的维护和管理有关。营业成本既包括营业费用(不包括直接生产成本)中的销货成本,也包括租金、工资及从原材料到维护费用等其他日常管理费用。营业成本不包括与利息、投资或外币折算等与融资有关的非营业费用。
The operating cost is deducted from revenue to arrive at operating income and is reflected on a company’s income statement.
总收入减去营业收入即为营业成本,营业成本反映在公司的利润表上。
KEY TAKEAWAYS
文章要点
Operating costs are the ongoing expenses incurred from the normal day-to-day of running a business that include both overhead and costs of goods sold (COGS).
营业成本是企业在正常的日常经营业务过程中发生的持续性费用,包括日常管理费用和销货成本。
Common operating costs in addition to COGS may include rent, equipment, inventory costs, marketing, payroll, insurance, and funds allocated for research and development; and exclude non-operating costs.
除销货成本以外的一般营业成本可能包括租金、设备、库存成本、营销、工资、保险和研发资金;不包括非营业成本。
Operating costs can be found and analyzed by looking at a company's income statement.
可以通过查看公司的利润表来查找并分析营业成本。
营业费用
Operating Expenses
Formula and Calculation for Operating Cost
营业成本的计算公式和计算步骤
Use the following formula and steps to calculate the operating cost of a business. You will find the information needed from the firm's income statement that is used to report the financial performance for the accounting period.
通过以下公式和步骤计算公司的营业成本。以下所需信息可从公司的利润表(用以报告公司在某一会计年度的财务状况)中获得。
Operating cost = Cost of goods sold +Operating expenses
营业成本=销货成本+营业费用
From a company's income statement take the total cost of goods sold, which can also be called cost of sales.
从公司的利润表中找到总销货成本,也叫总销售成本。
Find total operating expenses, which should be farther down the income statement.
找到总营业费用,一般在利润表的下方。
Add total operating expenses and cost of goods sold or COGS to arrive at the total operating costs for the period.
将总营业费用和销货成本相加,获得当期的总营业成本。
Deciphering Operating Costs
解读营业成本
Businesses have to keep track of operating costs as well as the costs associated with non-operating activities, such as interest expenses on a loan. Both costs are accounted for differently in a company's books, allowing analysts to determine how costs are associated with revenue-generating activities and whether or not the business can be run more efficiently.
企业必须时刻掌握其营业成本以及与非营业活动相关的成本,如贷款利息。这两项成本在公司的账簿中分别列示,因而分析员们可以确定有多少成本与创造收入的活动有关,以及业务是否可以实现更高效的运营。
Generally speaking, a company’s management will seek to maximize profits for the company. Because profits are determined both by the revenue that the company earns and the amount the company spends in order to operate, profit can be increased both by increasing revenue and by decreasing operating costs. Because cutting costs generally seems like an easier and more accessible way of increasing profits, managers will often be quick to choose this method.
一般来说,公司的管理层往往会寻求公司利益最大化。由于利润由公司所赚取的收入以及公司的经营支出决定,因此可以通过增加收入及减少营业成本来增加利润。而缩减成本往往看起来比增加收入更容易实现,因此管理层通常会很快地做出这个选择。
However, trimming operating costs too much can reduce a company’s productivity and, thus, its profit as well. While reducing any particular operating cost will usually increase short-term profits, it can also hurt the company’s earnings in the long-term. For example, if a company cuts its advertising costs its short-term profits will likely improve, as it is spending less money on operating costs.
然而,营业成本若缩减太多,则会降低公司的生产力,从而降低利润。尽管减少任何特定的营业成本会在短期内增加公司利润,但也有可能会损害公司的长期收益。例如,若一家公司减少其广告成本,短期来看由于其营业成本有所减少,其利润可能会增加。
However, by reducing its advertising, the company might also reduce its capacity to generate new business and earnings in the future could suffer. Ideally, companies look to keep operating costs as low as possible while still maintaining the ability to increase sales.
然而,广告成本的缩减有可能使这家公司开发新业务的能力降低,还可能使其未来的利润受到影响。理想情况下,公司往往希望在保持增加销售能力的同时尽可能降低营业成本。
Operating Costs Components
营业成本构成
While operating costs generally do not include capital outlays, they can include many components of operating expenses including:
尽管营业成本一般不包括资本支出,但可以包括营业费用的许多组成部分,其中包括:
Accounting and legal fees
会计和法律费用
Bank charges
银行手续费
Sales and marketing costs
销售和营销成本
Travel expenses
差旅费
Entertainment costs
招待费
Non-capitalized research and development expenses
非资本化研发费用
Office supply costs
办公用品费用
Rent
租金
Repair and maintenance costs
维修和保养费
Utility expenses
公共事业费
Salary and wage expenses
薪资
Operating costs will also include the cost of goods sold, which are the expenses directly tied to the production of goods and services. Some of the costs include:
营业成本也包括销货成本,销货成本指与商品和服务的生产直接挂钩的费用。其中一些成本包括:
Direct material costs
直接材料成本
Direct labor
直接劳动力成本
Rent of the plant or production facility
厂房或生产设施租金
Benefits and wages for the production workers
生产工人的福利和薪资
Repair costs of equipment
设备的维修成本
Utility costs and taxes of the production facilities
生产设施的公共事业费和税费
A business’s operating costs are comprised of two components, fixed costs and variable costs, which differ in important ways.
企业的营业成本由固定成本和变动成本两部分构成,这两部分具有很大的差异。
Fixed Costs
固定成本
A fixed cost is one that does not change with an increase or decrease in sales or productivity and must be paid regardless of the company’s activity or performance. For example, a manufacturing company must pay rent for factory space, regardless of how much it is producing or earning. While it can downsize and reduce the cost of its rent payments, it cannot eliminate these costs, and so they are considered to be fixed. Fixed costs generally include overhead costs, insurance, security, and equipment.
固定成本指的是不受业务量或生产力的增减变动而改变的、无论公司的经营活动或经营业绩如何均须支付的成本。例如,就一家制造业公司而言,无论其生产多少产品或获得多少利润,都必须要支付厂房租金。虽然它可以缩小规模,降低租金成本,但却不能完全消除这些成本,因此,这些成本被视为固定成本。固定成本一般包括日常管理费用、保险、安保和设备费用。
Fixed costs can help in achieving economies of scale, as when many of a company’s costs are fixed the company can make more profit per unit as it produces more units. In this system, fixed costs are spread out over the number of units produced, making production more efficient as production increases by reducing the average per-unit cost of production. Economies of scale can allow large companies to sell the same goods as smaller companies for lower prices.
固定成本可以促进规模经济的实现。当一家公司的许多成本都是固定成本时,这家公司每生产更多单位的产品就能创造更多的利润。在这一体系中,固定成本分摊到生产的产品单位的数量上,通过降低每单位的生产成本增加产量,从而提高生产效率。规模经济可以让大公司以更低的价格出售与小公司相同的产品。
The economies of scale principle can be limited in that fixed costs generally need to increase with certain benchmarks in production growth. For example, a manufacturing company that increases its rate of production over a specified period will eventually reach a point where it needs to increase the size of its factory space in order to accommodate the increased production of its products.
但由于固定成本一般会随着产量增长的某些基准而增长,因此规模经济也是会受到限制的。例如,在一特定时期内提高其生产率的一家制造业公司最终会在某个时候需要扩大工厂规模才能实现产品产量的提高。
Variable Costs
变动成本
Variable costs, like the name implies, are comprised of costs that vary with production. Unlike fixed costs, variable costs increase as production increases and decrease as production decreases. Examples of variable costs include raw material costs, payroll, and the cost of electricity. For example, in order for a fast-food restaurant chain that sells French fries to increase its fry sales, it will need to increase its purchase orders of potatoes from its supplier.
变动成本,顾名思义,指随着产量变化而变化的成本。与固定成本不同,变动成本会随着产量的增加或减少而增加或减少。变动成本包括原材料成本、工资和电费。例如,一家卖炸薯条的快餐店若要增加炸薯条的销量,则需要从其供应商处购买更多的土豆。
It's sometimes possible for a company to achieve a volume discount or "price break" when purchasing supplies in bulk, wherein the seller agrees to slightly reduce the per-unit cost in exchange for the buyer’s agreement to regularly buy the supplies in large amounts. As a result, the agreement might diminish the correlation somewhat between an increase or decrease in production and an increase or decrease in the company’s operating costs. For example, the fast-food company may buy its potatoes at $0.50 per pound when it buys potatoes in amounts of less than 200 pounds.
进行大批量采购时,公司有时也可能会获得批量折扣或“批发价”,即卖方同意减少每单位成本,以换取买方同意定期大批量采购。有鉴于此,这种情况可能会减少产量的增减与公司营业成本增减之间的相关性。例如,土豆购买量少于200磅时,快餐店购买土豆的价格为每磅0.5美元。
However, the potato supplier may offer the restaurant chain a price of $0.45 per pound when it buys potatoes in bulk amounts of 200 to 500 pounds. Volume discounts generally have a small impact on the correlation between production and variable costs and the trend otherwise remains the same.
但是,快餐店的土豆购买量达到200-500磅时,土豆供应商可能会以每磅0.45美元的价格向快餐连锁店供应土豆。批量折扣对产量和变动成本之间的相关性的影响通常较小。此外,趋势是会保持不变的。
Typically, companies with a high proportion of variable costs relative to fixed costs are considered to be less volatile, as their profits are more dependent on the success of their sales. In the same way, the profitability and risk for the same companies are also easier to gauge.
通常,人们会认为变动成本占固定成本比例高的公司更为稳定,因为这些公司的利润更多的取决于其销量,且它们的盈利能力和风险也更容易衡量。
Semi-Variable Costs
半变动成本
In addition to fixed and variable costs, it is also possible for a company’s operating costs to be considered semi-variable (or “semi-fixed.") These costs represent a mixture of fixed and variable components and, thus, can be thought of as existing between fixed costs and variable costs. Semi-variable costs vary in part with increases or decreases in production, like variable costs, but still exist when production is zero, like fixed costs. This is what primarily differentiates semi-variable costs from fixed costs and variable costs.
除固定和变动成本外,公司的营业成本也包括半变动成本(或“半固定成本”)。半变动成本是一种同时包含固定成本和变动成本因素的混合成本,可被视为介于固定成本和变动成本之间的成本。随着产量增加或减少,半变动成本部分会发生变化(如可变成本),但即使产量为零也依然存在(如固定成本)。这就是半变动成本与固定成本和变动成本之间的主要区别。
An example of semi-variable costs is overtime labor. Regular wages for workers are generally considered to be fixed costs, as while a company’s management can reduce the number of workers and paid work-hours, it will always need a workforce of some size to function. Overtime payments are often considered to be variable costs, as the number of overtime hours that a company pays its workers will generally rise with increased production and drop with reduced production. When wages are paid based on conditions of productivity allowing for overtime, the cost has both fixed and variable components and are therefore considered to be semi-variable costs.
加班就属于半变动成本。工人的固定薪资通常被视为固定成本,因此尽管公司管理层可以减少工人数量以及带薪工作时间,但公司仍然需要一定数量的劳动力保持运作。加班工资常常被视为可变成本,因为公司支付的加班工资通常会随着产量的增减而增减。如果薪资是基于允许加班的生产力条件支付的,则成本中会同时包含固定成本和变动成本因素,因而会被视为半变动成本。
Real World Example
真实示例
Below is the income statement for Apple Inc. (AAPL) as of December 29, 2018, according to their 10Q report:
以下是苹果公司截至2018年12月29日的利润表(资料来源:苹果公司10Q报表):
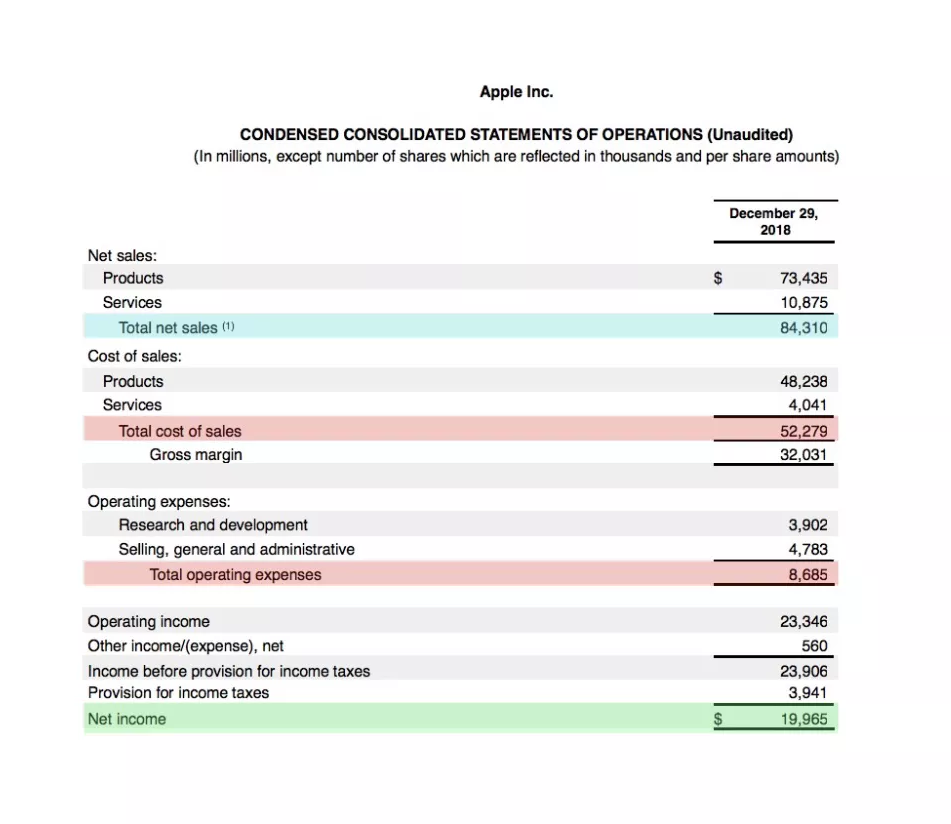
lApple reported total revenue or net sales of $84.310 billion for the period (highlighted in blue).
苹果公司报告称当期的总收入或净销售额为843.1亿美元(蓝色高亮显示)
lThe total cost of sales (or cost of goods sold) was $52.279 billion, while total operating expenses were $8.685 billion (in red).
总销售成本(或销货成本)为522.79亿美元,总营业费用为86.85亿美元(红色高亮显示)。
lWe calculate operating cost as $52.279 billion (COS) + $8.685 billion (OPEX).
我们计算的营业成本为522.79亿美元+86.85亿美元
lOperating costs were $60.964 billion for the period.
当期营业成本为609.64亿美元。
Apple Example Operating Costs. Investopedia
苹果营业成本示例。Investopedia
Apple's total operating costs must be examined over several quarters to get a sense of whether the company is managing its operating costs effectively. Also, investors can monitor operating expenses and cost of goods sold (or cost of sales) separately to determine whether costs are either increasing or decreasing over time.
需要对苹果公司几个季度以来的总营业成本进行审阅才能清楚苹果公司是否有有效地管理其营业成本。同时,投资者还可以分别监控营业费用和销货成本(或销售成本),确定成本是否随时间的变化而有所增减。
SG&A vs. Operating Costs
销售、一般和管理费用与营业成本
Selling, general, and administrative expense (SG&A) is reported on the income statement as the sum of all direct and indirect selling expenses and all general and administrative expenses (G&A) of a company. It includes all the costs not directly tied to making a product or performing a service—that is, SG&A includes the costs to sell and deliver products or services, in addition to the costs to manage the company.
销售、一般和管理费用在损益表中作为公司所有直接和间接的销售费用以及所有一般和管理费用的总和列报,其中包括与制造产品或履行服务没有直接联系的所有成本——即,除公司管理成本外,销售、一般和管理费用还包括销售、交付产品或服务的成本。
SG&A includes nearly everything that isn't in the cost of goods sold (COGS). On the other hand, operating costs include COGS plus all operating expenses including SG&A.
销售、一般和管理费用几乎包含销货成本以外的所有费用。另一方面,营业成本包含销货成本加包含销售、一般和管理费用在内的所有营业费用/
Limitations of Operating Costs
营业成本的局限性
As with any financial metric, operating costs must be compared over multiple reporting periods to get a sense of any trend. Companies sometimes can cut costs for a particular quarter thus inflating their earnings temporarily. Investors must monitor costs to see if they're increasing or decreasing over time while also comparing those results to the performance of revenue and profit.
与任何财务指标一样,营业成本也需要在多个报告期内进行比较方可判断出趋势。公司有时可以削减某个季度的成本从而暂时提高利润。投资者在将营业成本与收入和利润的表现进行比较时,必须监控成本的变化,看看成本是否随着时间的变化而有所增减。